

One of the most important ways homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint is by ensuring that the energy used to heat and cool their home is not wasted. Together, air sealing and insulation upgrades are effective tools to reduce your energy consumption and lower your carbon footprint.
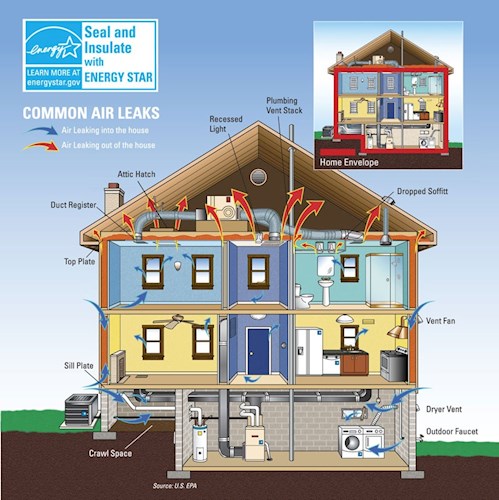
The average home has a variety of cracks and leaks that can cause drafts allows for air flow and opportunities for moisture to enter. Air sealing eliminates existing gaps by closing off leaks and drafts with caulking and weather stripping. Generally attics, basements, and crawl spaces offer the greatest chance to improve air sealing, though windows, doors, and heating ducts are also frequently leaky too. Additionally, air leaks are also often through chimneys, pipes, wires, and windows.

Insulation provides a thermal barrier inside the house so less heat is lost through the walls and roof. Properly insulating your home will decrease heat flow by providing an effective resistance to the flow of heat. An insulating material’s resistance to conductive heat flow is measured in terms of its thermal resistance or R-value. When the R-value is high, the insulation is more effective. The R-value depends on the type of insulation, its thickness, and its density. Installing more insulation in your home increases the R-value and the resistance to heat flow.
Learn more about how insulation works, types of insulation, and how to select what is appropriate for your home.
If you don’t know where to start a home energy audit is the best first step. A home energy audit, or energy assessment, can help you understand the whole picture of your home’s energy use and determine areas where your home can become more efficient.
The audit will reveal the areas for the greatest energy efficiency improvements and greatest potential energy savings. Then you can make a plan for how to prioritize making those upgrades over a number of years. In general home energy audits identify potential energy bills savings from 5-30%.
And remember, you may be eligible for up to $150 in tax credits through the Inflation Reduction Act for a home energy audit. Below, we linked a first hand account of a home energy audit written in the Associated Press.
You can receive up to $1,200 per year annually in tax credits for energy efficiency home improvements from the Inflation Reduction Act, including insulation (up to $1,200), exterior doors (up to $500), windows (up to $500), electrical panels (up to $600), and energy audits (up to $150).
Learn more about these tax credits and how they stack with Focus on Energy rebates.
Air sealing and insulating your home ensures your home’s heating and cooling systems are being used efficiently. But air sealing and insulation also confer a number of other benefits:
Comfort – Air sealing reduces drafts in your house, while insulation keeps your house more evenly heated/cooled so some rooms are not warmer or colder than others. This all translates to a cozier, more evenly climate-controlled home.
Lower energy costs – Air sealing and insulation is the most effective way to reduce your monthly energy costs. The Department of Energy found that for every $1 invested in weatherization you generate $1.72 in energy benefits and $2.78 in non-energy benefits, with an annual energy cost savings of $283 across the United States.
Reduced environmental impact – The best way to reduce your carbon footprint is to reduce your waste and consumption. Reducing your energy use is a great way to make a tangible impact to reduce your carbon footprint.
Lower maintenance costs – Leaks and drafts leave your house susceptible to rot and mold because water and moisture can leak in and cause damage. And in the winter, poorly insulated roofs can cause ice dams, which causes moisture to enter and the potential for long-term damage.
Human health – Protection from moisture and mold is an important component of the air quality in your home. Insulation and weatherization can reduce vulnerability to heat and cold-related illnesses. In addition, the ability to seal your home against outside contaminants is increasingly important as weather events like wildfires can cause poor air quality through a region.
Conserving energy within your home is an easy way to reduce your energy use. Focus on turning off appliances when they are not in use and by opting for energy-efficient appliances and electronics.

Energy for lighting can account for up to 10% of your electric bill. Consider upgrading your lighting to ENERGY STAR light-emitting diodes (LEDs) bulbs or energy-saving incandescents to reduce energy use. When shopping for bulbs, compare your choices using lumens. The higher the number of lumens, the brighter the bulb.
To get started you can receive a free Energy Pack from Focus on Energy.

You can save energy by making sure you look for the ENERGY STAR label on when purchasing new appliances like TVs, refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, etc. This symbol means that the appliance or electronic meets designated energy efficiency criteria.

Smart thermostats can help you use your home's heating and cooling system more efficiently. A smart thermostat is a Wi-Fi enabled device that automatically adjusts heating and cooling temperature settings in your home based on your needs. Smart thermostats that earn the ENERGY STAR label have been independently certified, based on actual field data, to deliver energy savings.
Focus on Energy is Wisconsin's statewide energy efficiency and renewable energy program. They offer technical assistance as well as have a variety of products for free and at reduced prices to help you reduce your household energy use, including: